芬兰图尔库大学的研究人员发现,[{” attribute=””>black hole in a binary system is tilted more than 40 degrees relative to the axis of stellar orbit. The finding challenges current theoretical models of black hole formation.
The observation by the researchers from Tuorla Observatory in Finland is the first reliable measurement that shows a large difference between the axis of rotation of a black hole and the axis of a binary system orbit. The difference between the axes measured by the researchers in a binary star system called MAXI J1820+070 was more than 40 degrees.
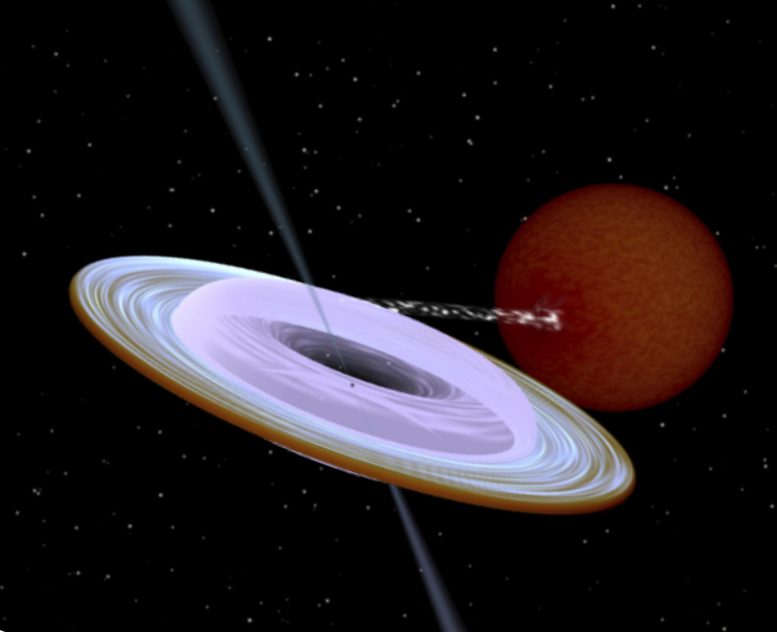

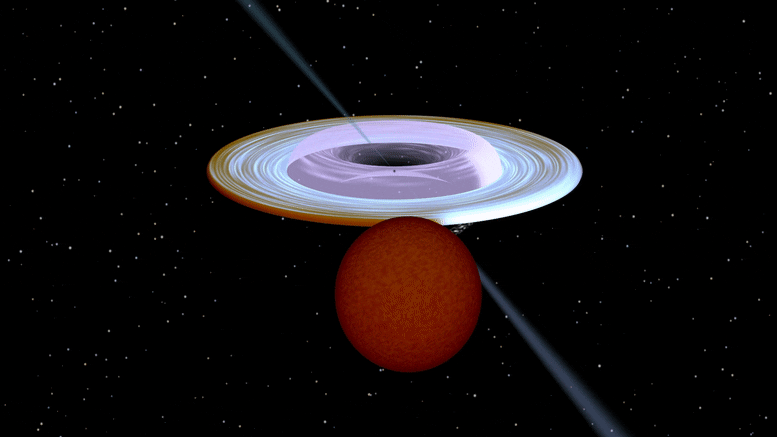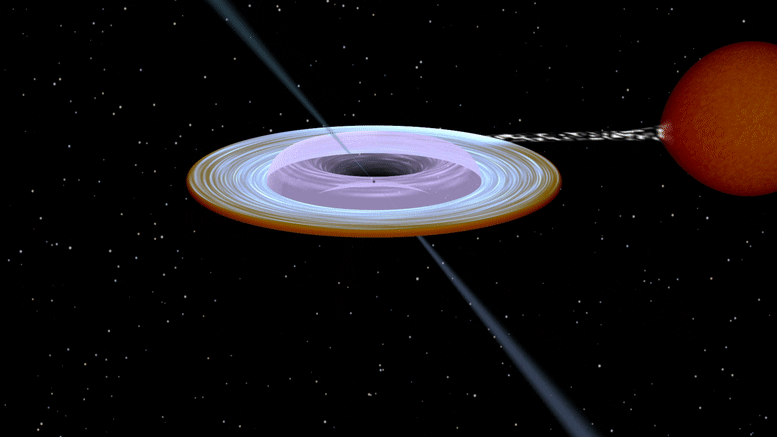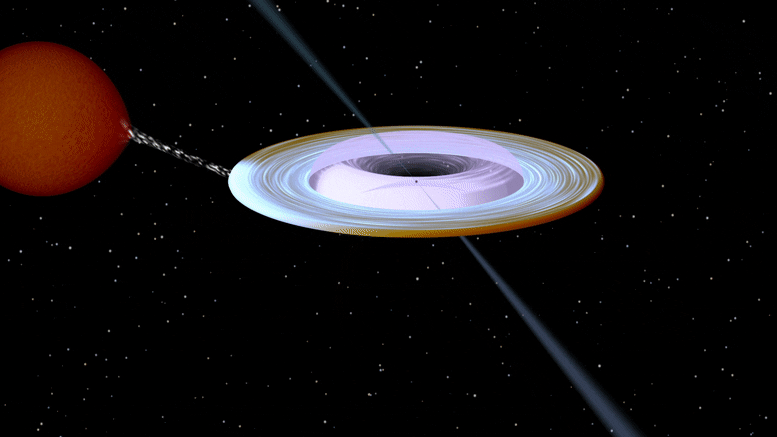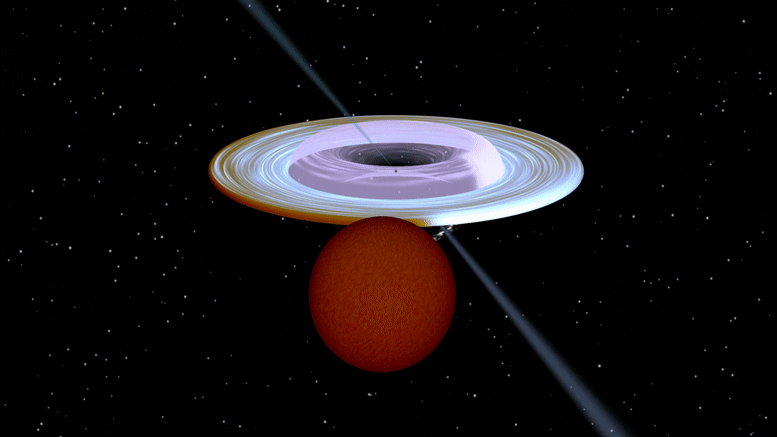
Artist impression of the X-ray binary system MAXI J1820+070 containing a black hole (small black dot at the center of the gaseous disk) and a companion star. A narrow jet is directed along the black hole spin axis, which is strongly misaligned from the rotation axis of the orbit. Image produced with Binsim. Credit: R. Hynes
Often for the space systems with smaller objects orbiting around the central massive body, the own rotation axis of this body is to a high degree aligned with the rotation axis of its satellites. This is true also for our solar system: the planets orbit around the Sun in a plane, which roughly coincides with the equatorial plane of the Sun. The inclination of the Sun rotation axis with respect to orbital axis of the Earth is only seven degrees.
“The expectation of alignment, to a large degree, does not hold for the bizarre objects such as black hole X-ray binaries. The black holes in these systems were formed as a result of a cosmic cataclysm – the collapse of a massive star. Now we see the black hole dragging matter from the nearby, lighter companion star orbiting around it. We see bright optical and X-ray radiation as the last sigh of the infalling material, and also radio emission from the relativistic jets expelled from the system,” says Juri Poutanen, Professor of Astronomy at the University of Turku and the lead author of the publication.
艺术家对 X 射线双星系统 MAXI J1820 + 070 的印象,该系统包含一个黑洞(气态盘中心的一个小黑点)和一颗伴星。 一条狭窄的射流沿着黑洞的旋转轴定向,该旋转轴与轨道的旋转轴强烈倾斜。 图像是轻而易举地制作出来的。 信用:R.海因斯
通过跟踪这些喷流,研究人员能够非常精确地确定黑洞旋转轴的方向。 当后来从伴星落入黑洞的气体量开始减少时,系统温度变冷,系统中很大一部分光来自伴星。 通过这种方式,研究人员能够使用光谱技术测量轨道的倾角,这与弹道的倾角大致吻合。
“要确定轨道的 3D 方向,还需要知道系统在天空中的位置角,这意味着系统如何相对于天空中的北方方向旋转。这是使用旋光技术测量的,”说尤里·波塔宁。
发表在《科学》杂志上的结果为研究这些系统的黑洞形成和演化开辟了有趣的前景,因为在许多黑洞形成和二元演化场景中很难获得这种极端的不平衡。
轨道轴与黑洞自转相差40多度,完全出乎意料。 科学家们在模拟黑洞周围弯曲时空中的物质行为时,通常认为这种差异非常小。 现有模型已经很复杂,现在新的发现正迫使我们为其添加一个新的维度,”Potanin 说。
参考:Guri Potanin、Alexandra Veledina、Andrei V Berdyugina、Svetlana V Berdyugina、Helen Germak、Peter J. Juncker、Gary JE Kagava、Ilya Kozenkov 的“X 射线双星 MAXI J1820+070 中的轨道-轨道黑洞旋转不平衡”, Vadim Kravtsov Filippo Perola、Manisha Shrestha、Manuel A. Perez-Torres 和 Serge S. Tsygankov,2022 年 2 月 24 日在此处提供。 知道.
DOI: 10.1126 / science.abl4679
主要结果是使用由图尔库大学与 奥胡斯大学 在丹麦。

“创作者。屡获殊荣的问题解决者。音乐布道者。无法治愈的内向。”




More Stories
应该早上锻炼还是晚上锻炼?
探索引力的“宇宙不平衡”
松鼠可能给中世纪的英国人带来了麻风病